What is UI (user interface) Design? is difficult to answer because of its large variety of misinterpretations. While User Experience is a mishmash of tasks focused on optimisation of a product for effective and enjoyable use; User Interface Design is its compliment, i.e. the look and feel, or the presentation and interactivity of the product. But it is easily and often confused by the industries that use UI Designers. To some extent that different job roles will often refer to the profession as something completely different (i.e.UX).
You will find perception of the profession that is alike to graphic design. Sometimes spreading to branding, and even front end web development as well.
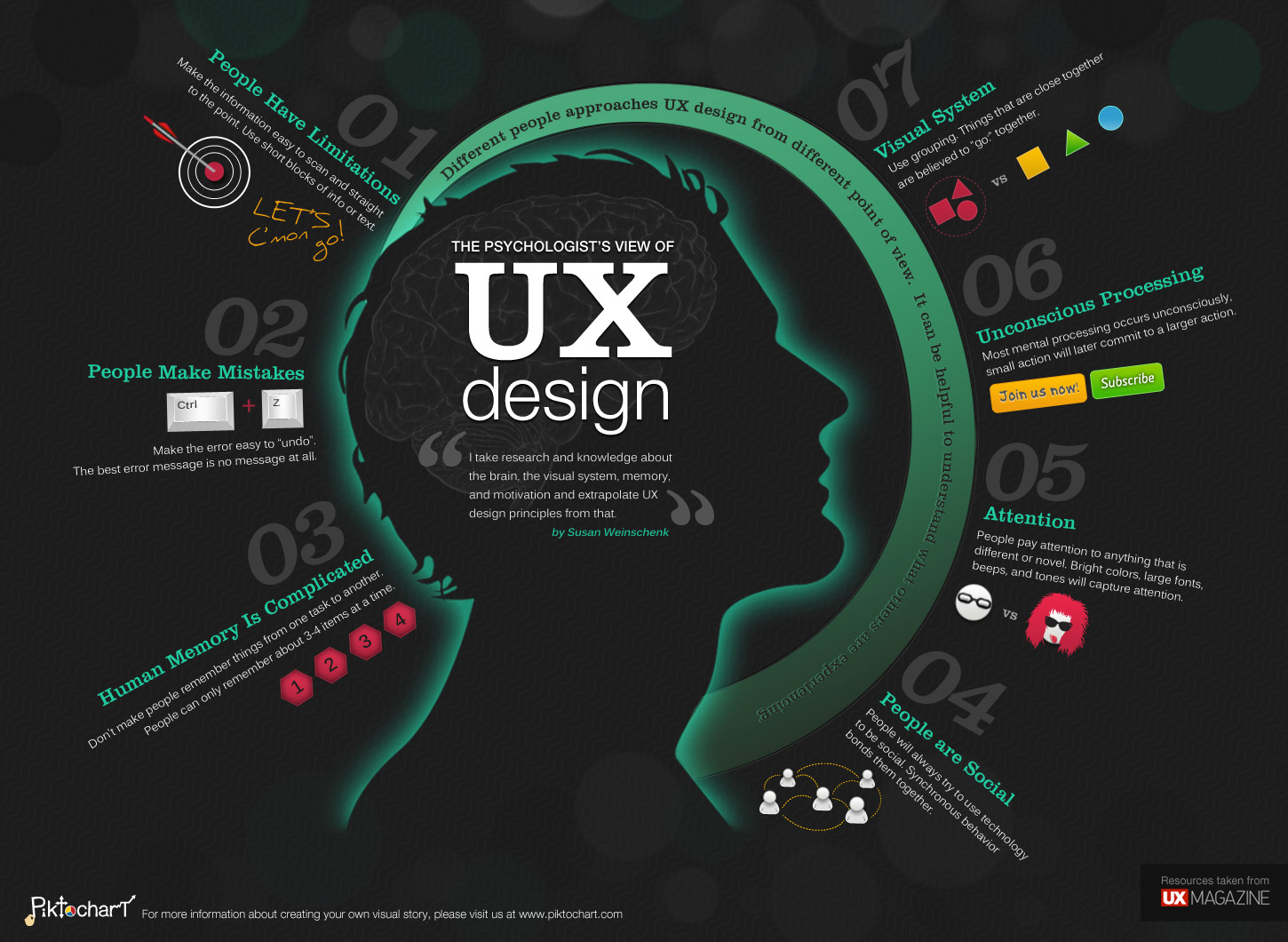
If you look at an expert explanation of User Interface Design, you will mostly find descriptions that are in part the same to User Experience. Even mirroring the same structural techniques.
So what is the right answer? The conflicting answer is: Neither of them.
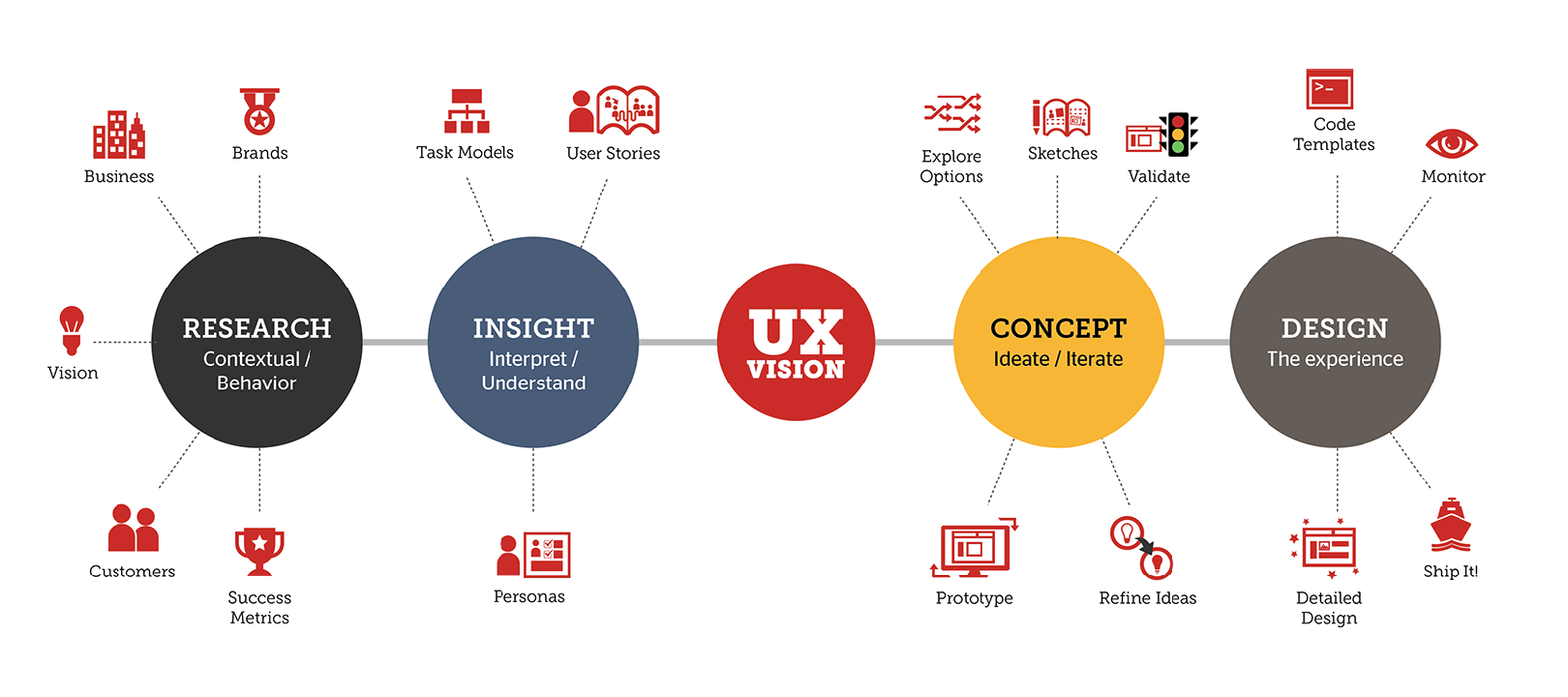
But both are close in minor ways. Like User Experience Design, User Interface Design is a all-round and challenging role. It is responsible for the transportation of a product’s research, development, content and layout into an appealing, guiding and responsive experience for a user. It is also a field that dissimilar to UX, is a strictly digital profession, as per how the dictionary defines it (as per below):
user interface
noun Computing
the means by which the user and a computer system interact, in particular the use of input devices and software.
Whether you choose UX design or UI design, it is important to understand how the other one works, and how to work with both of them.
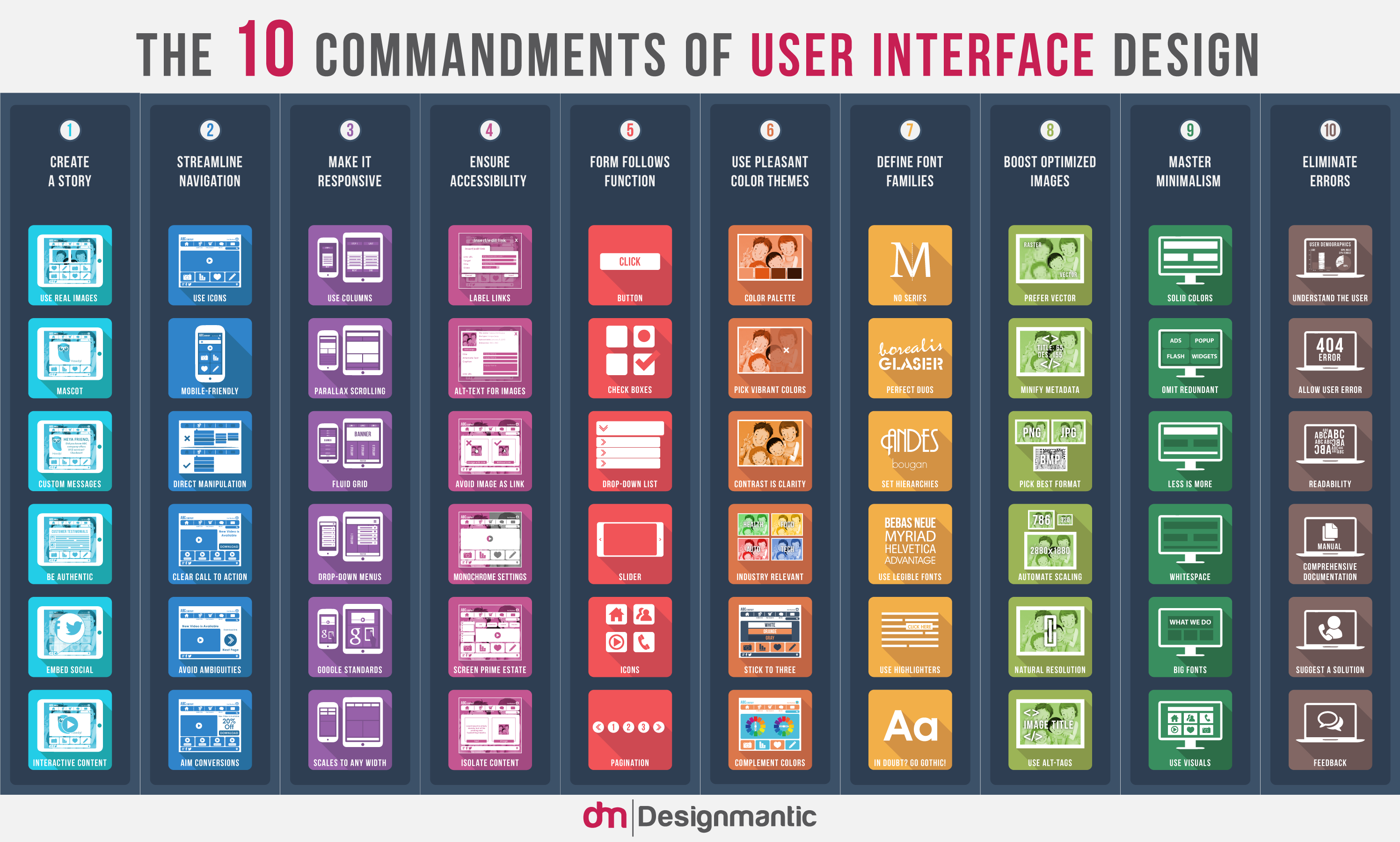
Below are some of a UI designer’s key responsibilities:
Look and Feel:
- Customer Analysis
- Branding and Graphic Design
- Design Research
- Branding and Graphic Design
- User Guides/Storyline
Interactivity and Responsiveness:
- Interactivity and Animation
- Implementation with Developer
- UI Prototyping
- Adaptation to All Device Screen Sizes
As a interactive and visual designer, the UI role is important to any digital interface and for customers a key element to trusting a brand. While the brand is never the responsibility of the UI designer, its translation to the product is.
A responsibility for “implementation” of the design with a developer is generally how UI have worked in the past, you should be aware that the lines are dim, as the term “Web Designer” (in short is a UI designer who can code) is being replaced by expertise of User Interface Designers. While UX has no need for coding, UI is a role that as time will progress, will rely on it as part of building interactive interfaces.