There is a new SEO sheriff in town and it’s name is Long tail keyword. What are these? These are longer and more specific keyword phrases that a visitor is more likely to use when they’re closer to buying or when they’re using voice search.
Google is constantly keeping us on our toes with all their algorithm updates, but one thing that has stayed pretty consistent for marketers looking to optimise their websites for the search engines is keyword research.
Well, the need to do keyword research has stayed the same. How you actually do it hasn’t.
What is keyword research?
Keyword research is when online users use keywords to find and research search terms that users enter into search engines. The knowledge about these specific search terms can help inform content strategy, and marketing strategy.
Below is a keyword research process you can follow to help you come up with a list of words you should be targeting.
This way, you will be able to establish a strong keyword strategy that helps you get found for the search terms you actually care about.
How do you research for keywords to suit you’re SEO strategy?
Step 1: Start by making a list of important and relevant topics based on what you know about your business.
Think about the topics you want to rank for. You can come up with about 5-10 topic keywords that you think are important for your business, and then you will use these topics to come up with some more targeted keywords later.
If you blog regularly then these are the keywords you blog about most often, or they could be the topics that come up the most in you sale conversations. Basically put yourself in the shoes of your buyer, what type of topics would your buyer or target audience search for to get your business found? If you were a company like us, for example keywords such as “graphic design” or “logo design” – you also might have general topics like “web design” or “SEO.
Step 2: Fill in those topics with keywords.
Now that you have a few topics you want to focus on, the next step is to identify some keywords that fall into those topics. These are keywords you think are important to rank for in the search engine results pages because your target audience is probably looking for those same terms.
For example, if we took that last topic for an graphic design agency – “graphic design” – I would brainstorm some keyword phrases that I think my customers would type in related to that topic. They might include:
- graphic design adelaide (location helps)
- logo design adelaide
- looking for graphic design
- need branding for my new business
- web designers in adelaide
- email marketing
- SEO experts
And so on and so on. The point of this exercise isn’t to come up with your final list of phrases – you just want to end up with a brain dump of phrases you think potential customers might use to search for content related to that particular topic.
Although more keywords are getting encrypted by Google each and every day, another intelligent way to come up with keywords is to find out which keywords your website is currently getting found for. To find this out you will need a website analytic like Google Analytics. Look into your website’s traffic sources, and search through you organic search traffic topics to identify the keywords user are using to arrive at your site.
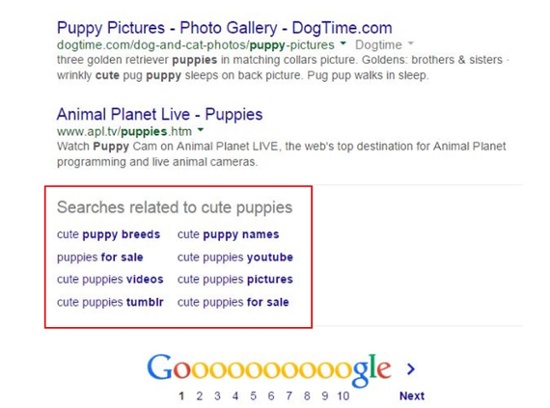
Step 3: Research related search terms.
If you’re finding it difficult to think of more keywords people might be searching for about a specific topic, go to Google.com and take a look at their related search terms that appear when you type in a keyword. When you type in your words and scroll to the bottom of Google’s results, you will notice some suggestions for searches related to your original input. These keywords can trigger ideas for other keywords you may want to take into consideration.
Step 4: Check for a combination of long-tail keywords and head terms.
Head terms are keywords phrases that are usually shorter and much more generic, they are typically just one to three words in length. Long-tail keywords are longer keyword phrases usually containing four or more words.
It’s important to check that you have a combination of long-tail terms and head terms because it’ll provide you with a keyword strategy that is well planned with long-term goals and short-term wins. This is because head terms are generally searched more frequently, making them often more competitive and harder to rank for than long-tail ones. Let’s take the following for example. Which of the following terms do you think would be more difficult to rank for?
- I need to find a graphic designer in Adelaide
- graphic design Adelaide
If you answered number 2, you’re right. But while head terms generally boost the most search volumes, the traffic you’ll get from the term “I need to find a graphic designer in Adelaide” is usually more enticing.
But Why?
Because if a user is looking for something that specific then they are probably a much more qualified searcher for your services than someone looking for something just generic. And because long-tail keywords tend to be more specific, it’s easier to tell what people who search for those keywords are really looking for. Someone searching for the head term “graphic design Adelaide,” on the other hand, could be searching it for a whole lot of other unrelated products or services than just your business.
Check your keyword lists to ensure you have a good mix of long-tail keywords and head terms. You definitely want some long-tail keywords, but you should also try to look at more difficult head terms over the long haul.
Step 5: How are your competitors ranking for the same keywords.
Just because a keyword is important to your competitor, it doesn’t necessarily mean it’s important to yours. But, understanding what keywords your competitors are trying to rank for is a good way to help you give your list of keywords another look.
If your competitor is ranking for similar keywords that are on your list, it definitely makes sense to work on improving your ranking for the same words. However, don’t ignore the words your competitors don’t seem to use much or don’t have. This could be a great way for you to own those important terms.
The ultimate goal is to end up with a list of keywords that provide some wins, but also help you make progress toward a bigger and more challenging SEO goal.
A great and free tool to use to see what keywords your competitors are ranking for is SEMrush, it allows you to run a number of free reports that show you the top keywords for the domain you enter.
Step 6: Use Google’s AdWords Keyword Planner to edit down your list.
So you have the right bag of keywords, it’s time to narrow down your lists with some more data. You have a lot of free tools at your disposal, but let me share our favourites.
We use Google AdWords Keyword Planner (you will need to set up an AdWords account for this though, but this does mean you have to create an ad) and Google Trends.
Use Google Keyword Planner to avoid any terms on your list that have way too little, or way too much, and don’t help you maintain a good mix like we talked about earlier. But before you do delete anything, just check out their trend history and projections using Google Trends. You can see whether some low-volume terms might actually be something you should consider.
Or perhaps you are just searching for a list of terms that is way too massive, and you have to narrow it down. Google Trends can help you determine which terms are trending upward, which are worth more of your focus.